Mi415 PRO




Mi415 PRO Turbidity Meter
Turbidity refers to the concentration of undissolved, suspended particles present in a liquid.
Turbidity is a measure of the clarity of a sample.
For potable water applications turbidity is a good indicator of water quality.
Turbidity Measurement is achieved by analyzing the amount of light refracted from suspended particles such as clay, silt and organic material.
By measuring turbidity, by photometric or tube methods, it is possible to estimate suspended solids content.
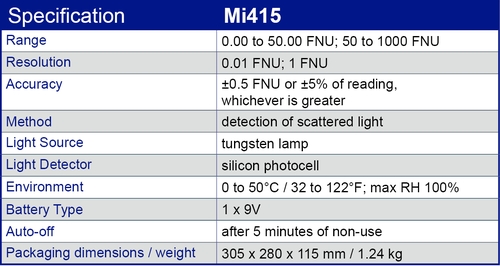
Mi415 has two operating ranges; 0.00 to 50.00 FNU, and 50 to 1000 FNU that can accommodate the most turbid condition you may encounter.
Mi415 is supplied in a hard carrying case, complete with reagents.
Introduction to Turbidity
The cloudy appearance of water (called Turbidity) is caused by suspended material.
The unit of measure adopted by the ISO Standard is the FNU (Formazine Nephelometric
Unit) and by EPA is NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Unit).
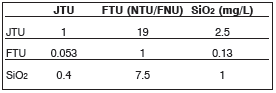
The other two methods used to test for turbidity and their measurement units are the JTU (Jackson Turbidity Unit) and the Silica unit (mg/L SiO2).
See the conversion table of these methods and their units for your reference.
Accessories:
- Mi515-100 0 FNU calibration solution, 30 mL
10 FNU, calibration solution, 30 mL
500 FNU, calibration solution, 30 mL - Mi0011 Glass cuvets (2 pcs)
- Mi0013 Stoppers for cuvets (2 pcs)
Ordering information:
Mi415 is supplied complete with 2 cuvets, reagents, hard carrying case, wiping tissue, 9V battery and instructions.